Abstract
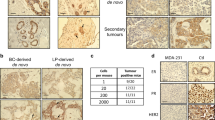
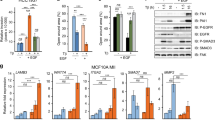
Activating mutations in the RAS family or BRAF frequently occur in many types of human cancers but are rarely detected in breast tumors. However, activation of the RAS–RAF–MEK–ERK MAPK pathway is commonly observed in human breast cancers, suggesting that other genetic alterations lead to activation of this signaling pathway. To identify breast cancer oncogenes that activate the MAPK pathway, we screened a library of human kinases for their ability to induce anchorage-independent growth in a derivative of immortalized human mammary epithelial cells (HMLE). We identified p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) as a kinase that permitted HMLE cells to form anchorage-independent colonies. PAK1 is amplified in several human cancer types, including 30--33% of breast tumor samples and cancer cell lines. The kinase activity of PAK1 is necessary for PAK1-induced transformation. Moreover, we show that PAK1 simultaneously activates MAPK and MET signaling; the latter via inhibition of merlin. Disruption of these activities inhibits PAK1-driven anchorage-independent growth. These observations establish PAK1 amplification as an alternative mechanism for MAPK activation in human breast cancer and credential PAK1 as a breast cancer oncogene that coordinately regulates multiple signaling pathways, the cooperation of which leads to malignant transformation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appledorn DM, Dao KH, O'Reilly S, Maher VM, McCormick JJ . (2010). Rac1 and Cdc42 are regulators of HRasV12-transformation and angiogenic factors in human fibroblasts. BMC Cancer 10: 13.
Arias-Romero LE, Villamar-Cruz O, Pacheco A, Kosoff R, Huang M, Muthuswamy SK et al. (2010). A Rac-Pak signaling pathway is essential for ErbB2-mediated transformation of human breast epithelial cancer cells. Oncogene 29: 5839–5849.
Bachman KE, Argani P, Samuels Y, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S et al. (2004). The PIK3CA gene is mutated with high frequency in human breast cancers. Cancer Biol Ther 3: 772–775.
Batzer AG, Rotin D, Urena JM, Skolnik EY, Schlessinger J . (1994). Hierarchy of binding sites for Grb2 and Shc on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol 14: 5192–5201.
Bekri S, Adelaide J, Merscher S, Grosgeorge J, Caroli-Bosc F, Perucca-Lostanlen D et al. (1997). Detailed map of a region commonly amplified at 11q13-->q14 in human breast carcinoma. Cytogenet Cell Genet 79: 125–131.
Beroukhim R, Getz G, Nghiemphu L, Barretina J, Hsueh T, Linhart D et al. (2007). Assessing the significance of chromosomal aberrations in cancer: methodology and application to glioma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 20007–20012.
Beroukhim R, Mermel CH, Porter D, Wei G, Raychaudhuri S, Donovan J et al. (2010). The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers. Nature 463: 899–905.
Boccaccio C, Ando M, Tamagnone L, Bardelli A, Michieli P, Battistini C et al. (1998). Induction of epithelial tubules by growth factor HGF depends on the STAT pathway. Nature 391: 285–288.
Boehm JS, Hession MT, Bulmer SE, Hahn WC . (2005). Transformation of human and murine fibroblasts without viral oncoproteins. Mol Cell Biol 25: 6464–6474.
Boehm JS, Zhao JJ, Yao J, Kim SY, Firestein R, Dunn IF et al. (2007). Integrative genomic approaches identify IKBKE as a breast cancer oncogene. Cell 129: 1065–1079.
Bokoch GM . (2003). Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 72: 743–781.
Bollag G, Clapp DW, Shih S, Adler F, Zhang YY, Thompson P et al. (1996). Loss of NF1 results in activation of the Ras signaling pathway and leads to aberrant growth in haematopoietic cells. Nat Genet 12: 144–148.
Bostner J, Ahnstrom Waltersson M, Fornander T, Skoog L, Nordenskjold B, Stal O . (2007). Amplification of CCND1 and PAK1 as predictors of recurrence and tamoxifen resistance in postmenopausal breast cancer. Oncogene 26: 6997–7005.
Brown LA, Kalloger SE, Miller MA, Shih Ie M, McKinney SE, Santos JL et al. (2008). Amplification of 11q13 in ovarian carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 47: 481–489.
Chattopadhyay I, Singh A, Phukan R, Purkayastha J, Kataki A, Mahanta J et al. (2010). Genome-wide analysis of chromosomal alterations in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma exposed to tobacco and betel quid from high-risk area in India. Mutat Res 696: 130–138.
Christensen JG, Schreck R, Burrows J, Kuruganti P, Chan E, Le P et al. (2003). A selective small molecule inhibitor of c-Met kinase inhibits c-Met-dependent phenotypes in vitro and exhibits cytoreductive antitumor activity in vivo. Cancer Res 63: 7345–7355.
Coles LC, Shaw PE . (2002). PAK1 primes MEK1 for phosphorylation by Raf-1 kinase during cross-cascade activation of the ERK pathway. Oncogene 21: 2236–2244.
Curto M, Cole BK, Lallemand D, Liu CH, McClatchey AI . (2007). Contact-dependent inhibition of EGFR signaling by Nf2/Merlin. J Cell Biol 177: 893–903.
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S et al. (2002). Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 417: 949–954.
Downward J . (2003). Targeting RAS signalling pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 3: 11–22.
Du J, Bernasconi P, Clauser KR, Mani DR, Finn SP, Beroukhim R et al. (2009). Bead-based profiling of tyrosine kinase phosphorylation identifies SRC as a potential target for glioblastoma therapy. Nat Biotechnol 27: 77–83.
Dummler B, Ohshiro K, Kumar R, Field J . (2009). Pak protein kinases and their role in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28: 51–63.
Elenbaas B, Spirio L, Koerner F, Fleming MD, Zimonjic DB, Donaher JL et al. (2001). Human breast cancer cells generated by oncogenic transformation of primary mammary epithelial cells. Genes Dev 15: 50–65.
Engelman JA, Chen L, Tan X, Crosby K, Guimaraes AR, Upadhyay R et al. (2008). Effective use of PI3K and MEK inhibitors to treat mutant Kras G12D and PIK3CA H1047R murine lung cancers. Nat Med 14: 1351–1356.
Favata MF, Horiuchi KY, Manos EJ, Daulerio AJ, Stradley DA, Feeser WS et al. (1998). Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. J Biol Chem 273: 18623–18632.
Freihoff D, Kempe A, Beste B, Wappenschmidt B, Kreyer E, Hayashi Y et al. (1999). Exclusion of a major role for the PTEN tumour-suppressor gene in breast carcinomas. Br J Cancer 79: 754–758.
Hennessy BT, Smith DL, Ram PT, Lu Y, Mills GB . (2005). Exploiting the PI3K/AKT pathway for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4: 988–1004.
Hirokawa Y, Tikoo A, Huynh J, Utermark T, Hanemann CO, Giovannini M et al. (2004). A clue to the therapy of neurofibromatosis type 2: NF2/merlin is a PAK1 inhibitor. Cancer J 10: 20–26.
Hoeflich KP, O'Brien C, Boyd Z, Cavet G, Guerrero S, Jung K et al. (2009). In vivo antitumor activity of MEK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors in basal-like breast cancer models. Clin Cancer Res 15: 4649–4664.
Hynes NE, MacDonald G . (2009). ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21: 177–184.
Johannessen CM, Boehm JS, Kim SY, Thomas SR, Wardwell L, Johnson LA et al. (2010). COT drives resistance to RAF inhibition through MAP kinase pathway reactivation. Nature 468: 968–972.
Kim DH, Muto M, Kuwahara Y, Nakanishi Y, Watanabe H, Aoyagi K et al. (2006). Array-based comparative genomic hybridization of circulating esophageal tumor cells. Oncol Rep 16: 1053–1059.
Kim SY, Dunn IF, Firestein R, Gupta P, Wardwell L, Repich K et al. (2010). CK1epsilon is required for breast cancers dependent on beta-catenin activity. PLoS One 5: e8979.
Kissil JL, Johnson KC, Eckman MS, Jacks T . (2002). Merlin phosphorylation by p21-activated kinase 2 and effects of phosphorylation on merlin localization. J Biol Chem 277: 10394–10399.
Kissil JL, Wilker EW, Johnson KC, Eckman MS, Yaffe MB, Jacks T . (2003). Merlin, the product of the Nf2 tumor suppressor gene, is an inhibitor of the p21-activated kinase, Pak1. Mol Cell 12: 841–849.
Knoll JH, Lichter P . (2005). In situ hybridization to metaphase chromosomes and interphase nuclei. Curr Protoc Hum Genet Chapter 4: Unit 4 3.
Lambros MB, Fiegler H, Jones A, Gorman P, Roylance RR, Carter NP et al. (2005). Analysis of ovarian cancer cell lines using array-based comparative genomic hybridization. J Pathol 205: 29–40.
Lau KS, Haigis KM . (2009). Non-redundancy within the RAS oncogene family: insights into mutational disparities in cancer. Mol Cells 28: 315–320.
McClatchey AI . (2007). Neurofibromatosis. Annu Rev Pathol 2: 191–216.
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J . (2000). The EGF receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene 19: 6550–6565.
Miron A, Varadi M, Carrasco D, Li H, Luongo L, Kim HJ et al. (2010). PIK3CA mutations in in situ and invasive breast carcinomas. Cancer Res 70: 5674–5678.
Mirzoeva OK, Das D, Heiser LM, Bhattacharya S, Siwak D, Gendelman R et al. (2009). Basal subtype and MAPK/ERK kinase (MEK)-phosphoinositide 3-kinase feedback signaling determine susceptibility of breast cancer cells to MEK inhibition. Cancer Res 69: 565–572.
Miyakis S, Sourvinos G, Spandidos DA . (1998). Differential expression and mutation of the ras family genes in human breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 251: 609–612.
Moffat J, Grueneberg DA, Yang X, Kim SY, Kloepfer AM, Hinkle G et al. (2006). A lentiviral RNAi library for human and mouse genes applied to an arrayed viral high-content screen. Cell 124: 1283–1298.
Neve RM, Holbro T, Hynes NE . (2002). Distinct roles for phosphoinositide 3-kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase and p38 MAPK in mediating cell cycle progression of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 21: 4567–4576.
Santen RJ, Song RX, McPherson R, Kumar R, Adam L, Jeng MH et al. (2002). The role of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 80: 239–256.
Scheid MP, Woodgett JR . (2001). Phosphatidylinositol 3′ kinase signaling in mammary tumorigenesis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 6: 83–99.
Schraml P, Schwerdtfeger G, Burkhalter F, Raggi A, Schmidt D, Ruffalo T et al. (2003). Combined array comparative genomic hybridization and tissue microarray analysis suggest PAK1 at 11q13.5-q14 as a critical oncogene target in ovarian carcinoma. Am J Pathol 163: 985–992.
Shaw RJ, Paez JG, Curto M, Yaktine A, Pruitt WM, Saotome I et al. (2001). The Nf2 tumor suppressor, merlin, functions in Rac-dependent signaling. Dev Cell 1: 63–72.
Sos ML, Fischer S, Ullrich R, Peifer M, Heuckmann JM, Koker M et al. (2009). Identifying genotype-dependent efficacy of single and combined PI3K- and MAPK-pathway inhibition in cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 18351–18356.
Tang Y, Chen Z, Ambrose D, Liu J, Gibbs JB, Chernoff J et al. (1997). Kinase-deficient Pak1 mutants inhibit Ras transformation of Rat-1 fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol 17: 4454–4464.
Trusolino L, Bertotti A, Comoglio PM . (2010). MET signalling: principles and functions in development, organ regeneration and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11: 834–848.
Tu HF, Chang KW, Chiang WF, Liu CJ, Yu EH, Liu ST et al. (2011). The frequent co-expression of the oncogenes PIK3CA and PAK1 in oral carcinomas. Oral Oncol 47: 211–216.
Vadlamudi RK, Adam L, Wang RA, Mandal M, Nguyen D, Sahin A et al. (2000). Regulatable expression of p21-activated kinase-1 promotes anchorage-independent growth and abnormal organization of mitotic spindles in human epithelial breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 275: 36238–36244.
Weidner KM, Di Cesare S, Sachs M, Brinkmann V, Behrens J, Birchmeier W . (1996). Interaction between Gab1 and the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase is responsible for epithelial morphogenesis. Nature 384: 173–176.
Weinman EJ, Hall RA, Friedman PA, Liu-Chen LY, Shenolikar S . (2006). The association of NHERF adaptor proteins with g protein-coupled receptors and receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Physiol 68: 491–505.
Xiao GH, Beeser A, Chernoff J, Testa JR . (2002). p21-activated kinase links Rac/Cdc42 signaling to merlin. J Biol Chem 277: 883–886.
Yamauchi T, Ueki K, Tobe K, Tamemoto H, Sekine N, Wada M et al. (1997). Tyrosine phosphorylation of the EGF receptor by the kinase Jak2 is induced by growth hormone. Nature 390: 91–96.
Zang M, Gong J, Luo L, Zhou J, Xiang X, Huang W et al. (2008). Characterization of Ser338 phosphorylation for Raf-1 activation. J Biol Chem 283: 31429–31437.
Zang M, Hayne C, Luo Z . (2002). Interaction between active Pak1 and Raf-1 is necessary for phosphorylation and activation of Raf-1. J Biol Chem 277: 4395–4405.
Acknowledgements
We thank Nicole A Spardy, Christine L Nguyen and Yaara C Zwang for critical reading of the manuscript. We also thank the Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center Cytogenetics Core for their assistance with fluorescence in situ hybridization studies. This work was supported in part by a Department of Defense Breast Cancer Research Program Pre-doctoral Fellowship (W81XWH-08-1-0767, YS), grants from the US National Cancer Institute (R33 CA128625 and R01 CA130988, WCH) and a Cancer Center Support Grant no. NIH 5 P30 CA06516 (Cytogenetics Core).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
WCH, KP, JJZ and RB are consultants for Novartis Pharmaceuticals.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shrestha, Y., Schafer, E., Boehm, J. et al. PAK1 is a breast cancer oncogene that coordinately activates MAPK and MET signaling. Oncogene 31, 3397–3408 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.515
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.515
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pak1 pathway hyper-activation mediates resistance to endocrine therapy and CDK4/6 inhibitors in ER+ breast cancer
npj Breast Cancer (2023)
-
Catechol-O-methyl transferase suppresses cell invasion and interplays with MET signaling in estrogen dependent breast cancer
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
circSFMBT1 promotes pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis via targeting miR-330-5p/PAK1 axis
Cancer Gene Therapy (2021)
-
Blockage of PAK1 alleviates the proliferation and invasion of NSCLC cells via inhibiting ERK and AKT signaling activity
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2021)
-
Coordinated dysregulation of cancer progression by the HER family and p21-activated kinases
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2020)